Exosomes are extremely tiny cellular vesicles that are mainly wrapped by the cell’s inner membrane and then released to the outside of the cell. It contains a variety of biological molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, etc., which can transmit information between cells, regulate physiological processes and affect various physiological processes.
Neuromedicine research believes that exosomes are involved in the occurrence and development of a variety of nervous system diseases. These tiny vesicles can carry bioactive molecules in nerve cells and, through their release, affect the functions of other nerve cells, including inflammation regulation, cell damage and repair, including neurodegenerative diseases, stroke, brain trauma, etc.
In addition, exosomes are a potential diagnostic tool and therapeutic target in the field of neuromedicine. They can be detected in body fluids (such as blood and cerebrospinal fluid), which helps to understand and diagnose early neurological diseases and may provide new avenues for diagnosis and treatment. Currently, the biological science and medical fields are also exploring the application of exosomes in delivering therapeutic drugs or stem cell therapy to improve neurological diseases.
Exosome research findings
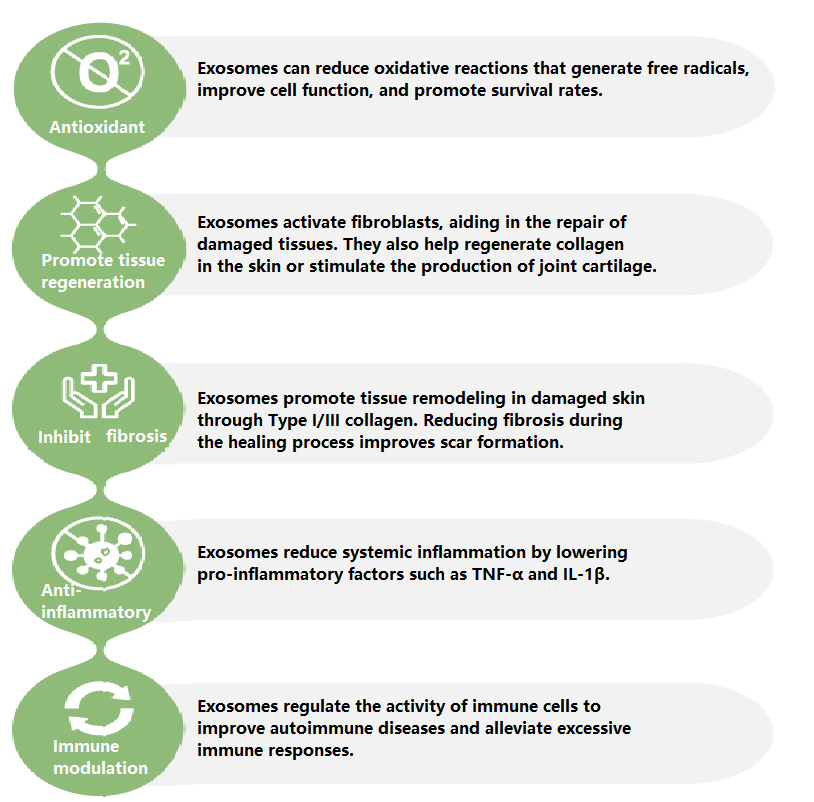
Research shows that exosomes are a tool that can transmit information between cells. They can carry a variety of biomolecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, and small signaling substances. These information transfer processes are essential for maintaining various physiological processes in the body, such as immune response, cell repair and growth.
✔Exosomes in the immune system: Studies have shown that exosomes play a key role in regulating immune responses. They can activate or suppress immune cells and help regulate inflammation and immune responses. This has potential therapeutic potential for the treatment of autoimmune and immune-related diseases.
✔Exosomes in tissue repair: Studies have shown that exosomes can promote tissue repair and regeneration. They can activate stem cells, promote repair of damaged areas, and help alleviate symptoms of some chronic conditions, such as heart and liver disease.
✔Exosomes in cancer research: Exosomes also have potential value in cancer research and treatment. They can play a key role in tumor growth and metastasis and thus serve as potential biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and treatment.
✔ Association of exosomes with neurological diseases: Some studies have shown that exosomes are associated with neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. They may play a role in the pathogenesis of the disease, which provides a new research direction for the treatment of these diseases.
Many studies have shown that exosomes play potentially important roles in maintaining human health and treating diseases. Although exosome research is still in its early stages, they may become one of the important breakthroughs in the fields of medicine and biology in the future.
Who are exosomes suitable for?
Exosome therapy is a relatively new medical approach that may be useful in the following situations:
🔸Inflammatory diseases: Exosomes may help alleviate the symptoms of inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis.
🔸 Neurological diseases: Exosome therapy is being studied to explore its potential therapeutic effects on neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
🔸Cancer: Exosomes can be used to deliver drugs or anti-cancer substances to attack cancer cells in a targeted manner and reduce damage to healthy tissues. Additionally, they may help diagnose and monitor cancer.
🔸Cardiovascular disease: Exosomes may play a role in the treatment of heart and vascular diseases, helping to repair damaged cardiovascular tissue.
🔸Immune system disorders: Exosomes may be used to regulate the immune system and treat autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus.
🔸Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine: Exosomes can be used to promote tissue repair and regeneration, such as bone, cartilage, and skin tissue.
🔸Acute or chronic kidney disease: Exosomes may be helpful in improving kidney function and alleviating symptoms in patients with kidney disease.
What is the process of exosome therapy?

🔸 Treatment preparation: Before receiving exosome therapy, patients usually need a preliminary evaluation to determine the suitability and safety of the treatment. Your doctor will take your medical history and may do some tests to make sure you have no contraindications.
🔸Exosome collection: Exosomes can be obtained from a variety of sources, including cell culture, plasma, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, etc. Exosome collection is not usually extremely painful, but some people may experience mild discomfort.
🔸Exosome processing: The collected exosomes need to be processed and purified to remove unnecessary components to ensure safety and effectiveness.
🔸Exosome delivery: Once the exosomes are prepared, they can be delivered to the patient through different routes. This may include intravenous injection, local injection, or other suitable method. The delivery of exosomes does not usually cause noticeable pain, but in some cases, there may be mild discomfort.
🔸Treatment time: The duration of a single exosome treatment will vary depending on each person’s treatment method, disease type, and patient condition. Some treatments may only take a few minutes, while others may take hours. The doctor will develop a treatment plan for the patient based on the specific situation.
🔸Postoperative wounds: Exosomes will not cause obvious external wounds. But if exosome collection requires puncture or sampling, there may be minor trauma, which is usually minor and heals in a short time.
Exosome therapy is an increasingly popular treatment modality in the medical and aesthetic fields, often used to improve skin texture, reduce wrinkles, enhance skin tone, and more. While this treatment is generally safe, there are some lifestyle and dietary considerations that can help you maximize the benefits and minimize potential discomfort.
Things to note after exosome treatment:
🔸Avoid direct sunlight: After exosome treatment, the skin may become sensitive and more susceptible to damage from the sun. Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun or use a high SPF sun protection product for one week after surgery.
🔸Avoid hot baths and steam baths: Avoid hot baths and steam baths during the first few days after your treatment as this may cause uneven skin tone.
🔸Do not touch or rub the skin: Avoid rubbing or massaging the treated area during the first few days after the treatment as this may cause pain or discomfort.
🔸Use mild cleansing products: One week after surgery, choose mild facial cleansers and cleansing products, and avoid products containing irritating ingredients. Also steer clear of too much makeup if possible.
🔸Moderate exercise: Mild exercise is fine, but avoid strenuous exercise to reduce sweating and the possible effects of excessive activity on the skin.
🔸Proper diet: Diet has an important impact on skin health. Eating foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and black tea, can help maintain healthy skin. At the same time, maintaining good water intake is also key to ensure that the skin is fully hydrated.
The professional medical team of the Marseille Quincé reminds that exosome therapy is still in the research and clinical trial stage, so there may be differences between different regions and medical institutions. If you are interested in exosome therapy or need to undergo such treatment, it is recommended to consult a professional doctor for detailed information and guidance. Furthermore, the pain levels and risks of treatment vary among individuals and may need to be assessed on a case-by-case basis. Most importantly, follow the advice of your doctor or therapist with whom you undergo exosome therapy. They will provide specific guidance based on your individual situation.
Learn more about: stem-cell-derived-exosomes